— 9 min read
Exploring Construction Robotics: Types, Benefits & Real-World Applications
Last Updated Nov 15, 2024
Last Updated Nov 15, 2024

Robotic technology has the potential to revolutionize every part of the construction industry – yet it can be hard to separate the buzz about the potential from the actual advantages of implementing new tools. Deciding if and how to adopt robotics starts with understanding the technology, being able to assess whether it’s a good investment, and understanding how it integrates into the larger tech ecosystem.
This article explores robotics in construction, including important considerations and challenges, plus key implementation strategies.
Table of contents
Types of Construction Robotics
Robotics in construction refers to the use of automated machines and systems to improve performance or create new possibilities related to tasks and workflows. Robotics encompasses a range of technologies and applications, ranging from simple, task-specific robots to advanced, autonomous systems.
At this point in the evolution of technology, robotics currently in use on construction sites are mostly semi-automated, meaning they can extend human capabilities but still require human supervision and input. These robots usually perform single tasks in ways that are more efficient and quick than humans or in ways that avoid putting humans in dangerous situations.
Reality Capture
One of the most common and effective uses of single-task robotics currently is in reality capture. Robotics mounted with cameras can be used to collect data on the jobsite through images, 3D scans or environmental readings.
Drones can be programmed to fly a set path every day or week to record site progress. On the ground, robotic “dogs” armed with 360 cameras can walk the jobsite, recording high-resolution images for a digital, 3D walkthrough.
These systems can often be paired with BIM software and augmented reality hardware to compare the installation with design side-by-side and in 3D, making it easier to identify potential clashes or deviations on a jobsite walk.
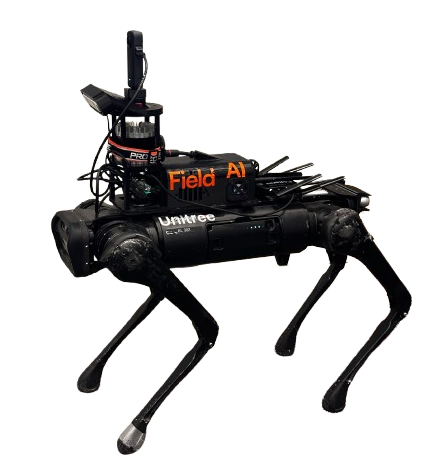

Examples:
Surveying & Site Layout
Laying out a site is traditionally a very deliberate, manual process — shooting grades, setting elevations, snapping chalk lines and marking penetrations, etc. — that can be time-consuming and subject to human error. Robots can automate certain surveying tasks. Others can take a digital site map or CAD/BIM file and print the layout on a concrete slab with precision.
Examples:
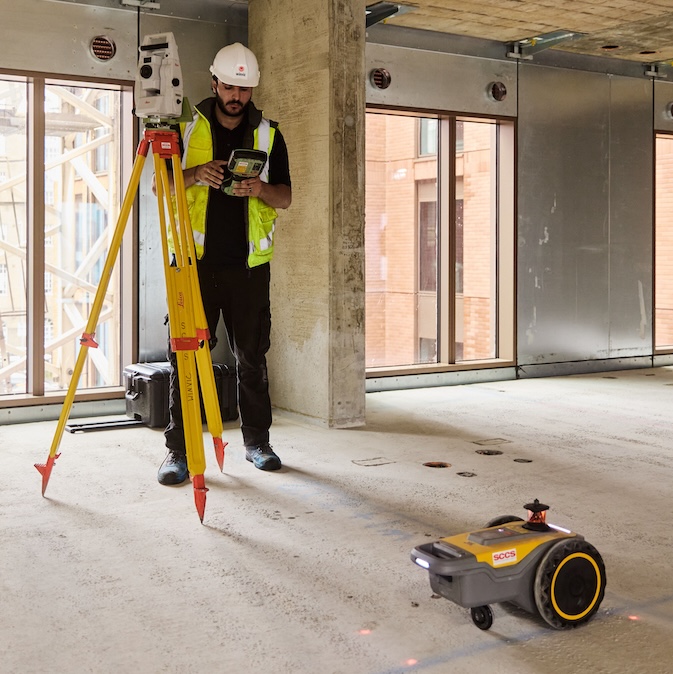

Installation & Quality Control
There are many examples of single-use robots currently available to assist with installation, including track-based rovers navigating job sites, robots taping drywall or machines drilling anchors. Robotics are also used in the creation of prefabricated elements, including cutting and shaping materials, assembly and quality control.
Examples:
Autonomous Systems
Fully automated robotics operate completely on their own, performing tasks without direct human direction or intervention. These systems can handle complex activities, such as autonomous equipment for grading or excavation.
When many people hear about robotics, this is the type they imagine in the form of robots that look like futuristic humanoids. However, most types of fully automated technology are still in the early stages of development and face challenges related to environmental adaptability or regulatory compliance.
Key Benefits of Robotics in Construction
Robotics should have a defined and measurable impact on a project or company. When implemented effectively, the benefits can be great.
Safety & Risk Management
Robotics can significantly improve safety and reduce the risk of injury on job sites by taking over dangerous tasks. For example, robots can handle jobs like drilling anchors in high places, minimizing the need for workers to get in potentially dangerous positions.
Robotics can significantly improve safety and reduce the risk of injury on job sites by taking over dangerous tasks. For example, robots can handle jobs like drilling anchors in high places, minimizing the need for workers to get into potentially dangerous positions.
Kris Lengieza
Vice President, Global Technology Evangelist
Procore Technologies
Increased Productivity
Robotics can expedite many processes and increase overall productivity. They can perform repetitive tasks quickly, accurately and without breaks, which can accelerate progress towards milestones and improve workflows.
Robotics can expedite many processes and increase overall productivity by performing repetitive tasks quickly, accurately, and without breaks, which can accelerate progress toward milestones and improve workflows.
Kris Lengieza
Vice President, Global Technology Evangelist
Procore Technologies
Rather than replacing human workers, robotics can enhance skilled labor by handling mundane, strenuous or dangerous tasks. This allows human workers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of projects.
Improved Accuracy & Quality Control
Robotics can significantly improve accuracy and quality control on the jobsite. Task-specific robots are frequently used to enhance precision by eliminating human errors associated with repetitive or complex tasks.
For instance, the use of robotic total stations for site layout allows for more accurate placement of building components. These robotic systems can cover more ground and facilitate precise layouts, reducing the likelihood of errors and rework.
When we made the change from traditional total stations to a robotic total station, the decision wasn't necessarily based on being able to perform tasks faster – it was about covering more ground and having more control, which subsequently reduced our risk. I obtained a demo unit, collected data in the field, and was able to demonstrate that the investment would pay for itself in under six months, giving us significantly more control over our processes.
Kris Lengieza
Vice President, Global Technology Evangelist
Procore Technologies
Cost reduction
Improving efficiency and reducing errors can lead to significant cost savings. Automated systems can help optimize material usage, reduce labor costs and minimize rework.
Sustainability
Optimizing resource use and reducing waste can increase the sustainability of a project. Automated processes can ensure precise material application, align work with sustainable building practices and reduce a project’s environmental impact.
Stay updated on what’s happening in construction.
Subscribe to Blueprint, Procore’s free construction newsletter, to get content from industry experts delivered straight to your inbox.
Keys to Adopting and Implementing Robotics in Construction
Robotics shouldn’t be adopted without a lot of consideration. They are often expensive to acquire and require a lot of time and energy to master. Robotics should be late-stage additions to a tech ecosystem, which should already have foundational components such as project management software and BIM tools that can inform and optimize the robot's ability to execute tasks and collect and analyze data.
Below are additional considerations before adoption or during implementation of robotics, including how to overcome common challenges.
Start with existing processes and workflows.
The impact of robotics is almost always maximized when applied to existing workflows. Using robotics on established procedures rather than entirely new ones isolates variables that can cause issues, allows for easier monitoring of efficacy, and means that team members and stakeholders already have the expertise to contribute to the process.
For example, a contractor investing in a robot for layout tasks should already have a site engineer performing layout tasks manually. That way, the new technology enhances the existing workflow, as opposed to creating a new one, with a human to supervise and intervene when necessary.
Demo and pilot the technology.
Whenever possible, conduct pilot projects or demos before full-scale adoption of robotics. This allows for a period of testing the efficacy of the tool and helps identify potential issues based on real-world performance.
For example, spending $20,000 to test a robot before spending $100,000 to own it is a good way to understand if the investment will ultimately be worth it. This step isn’t always possible, especially for smaller contractors, and often relies on a company having a dedicated budget and department for innovation.
Address team concerns.
Address workforce fears and misconceptions about robotics head-on by having transparent, open conversations. Explain the benefits of each new tool and how efficacy will be measured as a way to demonstrate its adoption is meant to aid workers – not replace them. This type of communication can also enlist worker expertise in implementing and maximizing the tools.
Provide training and guidance.
Invest in training programs to equip workers with the skills needed to operate and maintain robotic systems. This helps demonstrate an investment in workers’ futures with the company, while also leading to smoother integration and safer execution.
Humans are important parts of the implementation process to ensure the tool is meeting performance and regulatory requirements. Training helps them understand how to identify issues, measure success and analyze data.
Define the purpose.
The adoption of robotics should be aligned with clear project or business objectives, such as improved performance, increased safety or reduced cost. Robotics are usually best for jobs that are dull, dirty or dangerous, but can lead to unnecessary expenses when they are acquired and implemented without intent or used to launch a new procedure, as opposed to enhancing one that already exists.
Establish clear metrics.
The success or efficacy of robotics should be monitored through clearly defined metrics, such as measures of efficiency gains or cost savings. Collecting data on project costs, rework or timelines before introducing robotics can create simple ways to assess the difference once robotics have been implemented. For example, understanding how much time and money it takes for a site engineer to lay out a floor will help to assess the return on investment on a layout robot.
Create a system to collect and manage data.
Data collection and analysis should be standardized across projects. Reliable data helps to optimize robotic performance, achieve consistent results and address issues.
Most robotics require integration with artificial intelligence (AI), which requires the collection of reliable data in order to function effectively. AI enables adaptive navigation and decision-making for robots in dynamic situations and environments.
Consider logistics.
Even if a robot might be a good investment in theory, it’s important to understand if it will be good in practice. Consider the downtime that might come from maintenance, recharging, movement between sites or training to ensure the investment will get enough use — especially since mass deployment of robotics across all projects isn’t currently common.
Any conversation about equipment is ultimately an uptime versus downtime conversation. Maintenance, movement, and training time are downtime activities, while productive use of the robot is uptime. Think about your existing equipment and tools and how you move them from project to project. Construction companies need to think about robotics in the same way.
Kris Lengieza
Vice President, Global Technology Evangelist
Procore Technologies
The future of robotics starts with an open mind.
The current reality of robotics is far from its potential future. However, that future is fast-approaching, and promises never-before-seen efficiency, safety and sustainability. But even as new technologies emerge and costs drop, the successful adoption and deployment of robotics in the future will depend on the same mindsets it does now: an openness to new ways of thinking, a commitment to asking difficult questions and a dedication to careful planning, workforce engagement and effective data management.
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your submission.
0%
0%
You voted that this article was . Was this a mistake? If so, change your vote here.
Scroll less, learn more about construction.
Subscribe to The Blueprint, Procore’s construction newsletter, to get content from industry experts delivered straight to your inbox.
By clicking this button, you agree to our Privacy Notice and Terms of Service.
Categories:
Tags:
Written by
Kris Lengieza
Kris Lengieza is the Global Technology Evangelist at Procore Technologies. Kris brings a wealth of experience and passion to the intersection of construction and technology. Previously serving as the VP of Global Partnerships & Alliances, Kris oversaw a diverse ecosystem spanning channel, ISV, public, and association partnerships. His recognition as one of the Top 40 Construction Professionals Under 40 by ENR and BD&C underscores his impact in the industry. Kris’ journey began with 15 years working in the construction field, where he embraced technology as an early adopter and strived to seamlessly integrate data across all construction solutions. As a futurist and construction tech evangelist, Kris now collaborates extensively with industry innovators, tech organizations, and construction companies. Together, they explore transformative technologies that promise to revolutionize our work processes. Kris has played a pivotal role in Procore’s product strategy, delivering industry and technology insights to improve how Procore’s solutions serve the industry.
View profileJames Hamilton
70 articles
James Hamilton is a writer based in Brooklyn, New York with experience in television, documentaries, journalism, comedy, and podcasts. His work has been featured on VICE TV and on The Moth. James was a writer and narrator for the show, VICE News Tonight, where he won an Emmy Award and was nominated for a Peabody Award.
View profileExplore more helpful resources

Construction Invoice Factoring: A Quick Guide
Construction companies need to maintain consistent cash flow. Projects can take years to complete, and delays and unforeseen events may keep expenses mounting. Adding to this load are typically high upfront...

Understanding Subcontractor Bid Packages in Construction
Construction bid packages can have a cascading impact on the success of a construction project. The quality of a bid project may affect the quality of the bids, which in...

Tackling the Top 10 Construction Industry Issues
The construction industry is constantly evolving, bringing both opportunities and challenges. Companies must navigate an array of construction industry issues — from workforce shortages to integrating new technologies into their...

Mission Critical Construction: Strategies for Success
Mission critical construction involves building structures whose functions cannot afford to fail, as any disruptions can lead to significant consequences for society. Keeping data centers, hospitals, power plants and other...